In today's age of accessibility and convenience, over-the-counter (OTC) hearing aids offer hope to those needing hearing assistance. These devices can be bought without a prescription or professional fitting, promising a simpler path to better hearing. However, the decision to opt for OTC hearing aids should not be made lightly. Understanding their benefits and risks is crucial. Choosing the wrong option could potentially lead to inadequate hearing support. The significance of making an informed choice cannot be overstated, especially when it pertains to one's auditory health.
This article explores key aspects of OTC hearing aids, including their pros and cons. It emphasizes the importance of understanding your hearing loss before purchase and steps for achieving the best outcomes. The risks of using OTC hearing aids inappropriately are highlighted, along with the value of professional support. This guide helps readers decide if these devices meet their needs or if other options should be considered.
Understanding Your Hearing Loss
How to Self-Diagnose
Identifying hearing loss often begins with self-observation. Individuals may notice difficulty understanding conversations, especially in noisy environments. They may also find themselves frequently asking others to repeat themselves. Common signs include turning up the volume on phones or struggling to hear on calls. Instead of relying solely on self-diagnosis, it's essential to seek professional advice to confirm any hearing concerns.
Importance of Professional Hearing Tests
Professional hearing assessments are crucial for evaluating hearing capabilities across different frequencies and environments. An audiologist conducts tests such as speech and pure-tone audiometry to determine the nature and extent of hearing loss. These assessments help create a targeted treatment plan, including hearing aids, conservation strategies, or OTC options for mild cases.

Common Signs of Hearing Loss
Hearing loss can manifest through various signs that gradually become more apparent. Early indicators might include difficulty following conversations in crowded areas. Moreover, they frequently ask for repetitions during conversations, and a tendency to increase the volume on electronic devices. More subtle signs include feeling stressed or fatigued from straining to hear and misunderstanding spoken words. As hearing loss progresses, it may lead to social withdrawal due to the challenges in communication.
Pros of Using OTC Hearing Aids
Ease of Access
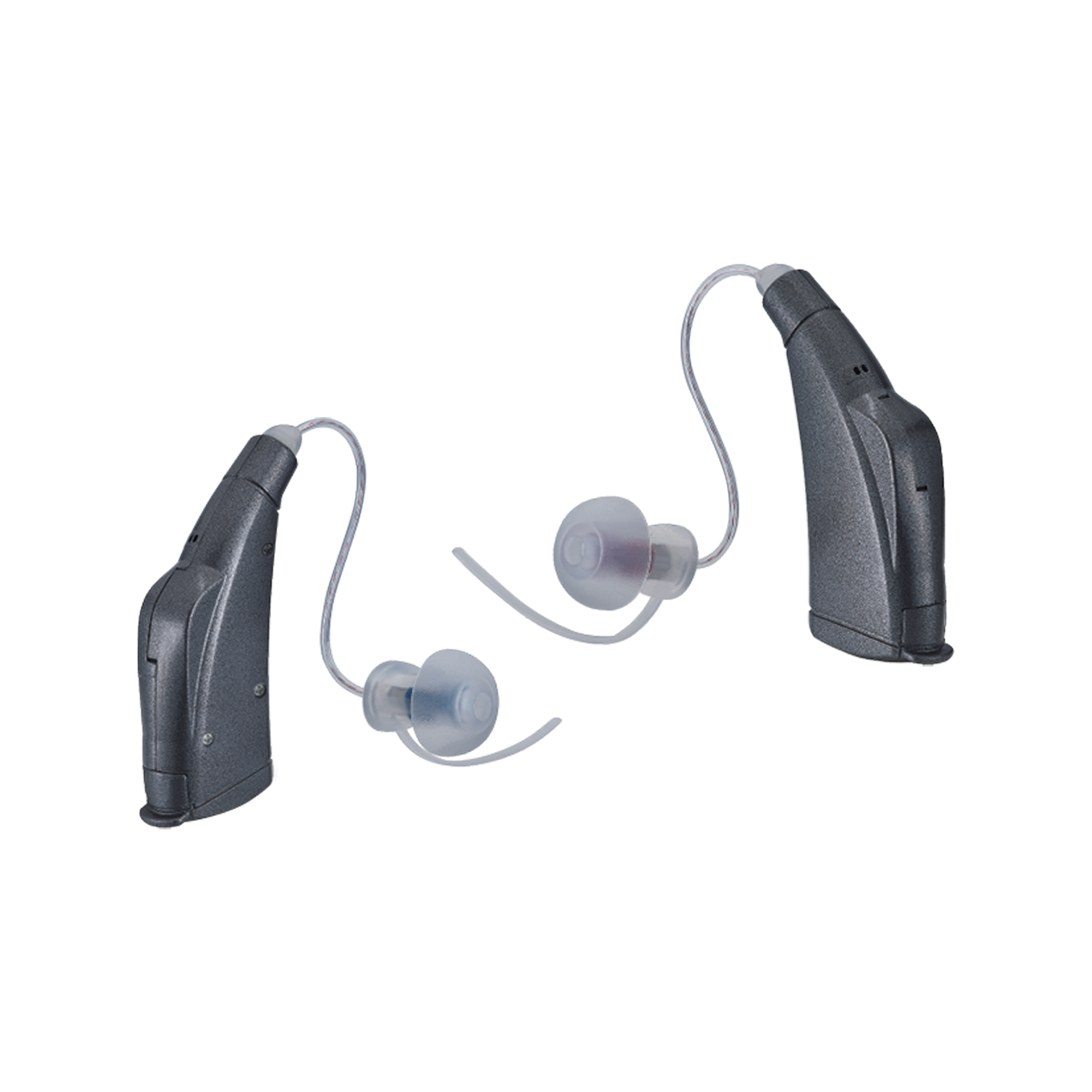
OTC hearing aids significantly enhance accessibility for individuals. These devices are FDA-approved for over-the-counter purchase. Consumers can now buy them directly in stores or online without a prescription. This simplifies access for those with mild to moderate hearing issues, enabling timely action. Direct availability is crucial to prevent worsening hearing loss.
Affordability
One of the most significant advantages of OTC hearing aids is their cost-effectiveness. These devices are generally available at lower price points compared to prescription hearing aids. Their affordability increases access, encouraging more people to use hearing aids who might otherwise go without this essential support.
Independence in Managing Hearing Loss
OTC hearing aids empower users to manage their hearing loss independently. Many devices include preset modes and smartphone apps. These features let users perform hearing tests and adjust settings themselves. Customization ensures the aids meet specific needs without professional assistance, giving users control over their auditory health.
Cons of Using OTC Hearing Aids
Risk of Misdiagnosis
OTC hearing aids empower users to manage their hearing loss independently. Many devices include preset modes and smartphone apps for hearing tests. Users can adjust the aids based on results, ensuring devices meet their specific needs. This customization fosters control over auditory health without needing professional assistance.
Potential for Overuse Damage
One significant risk associated with OTC hearing aids is the potential for overuse damage due to inadequate volume controls. Many OTC models lack advanced volume regulation, causing users to increase the volume to compensate for poor sound quality. This can lead to dangerously high sound levels, further harming hearing.
Limited Support and Customization
OTC hearing aids typically offer limited support and customization options compared to prescription counterparts. They are often sold without professional consultation or fitting, leading to discomfort and reduced effectiveness. Without personalized adjustments, these devices may not address specific hearing loss needs adequately.
Steps to Take Before Buying OTC Hearing Aids
Consider a Professional Hearing Test
Before purchasing OTC hearing aids, individuals should consider undergoing a professional hearing test. Many consumers cannot accurately assess their hearing loss alone. A diagnostic test by a licensed audiologist provides detailed information on the degree and type of hearing loss. These evaluations help determine the most suitable hearing aid for their needs.
Research Device Options
When exploring OTC hearing aid options, consider factors affecting user experience and satisfaction. Look for devices with clear packaging information. Packaging should include warnings, manufacturer contact details, return policies, and specifications like battery type. Evaluate features like waterproofing and comfort to avoid future complications.
Understand Trial and Return Policies
Understanding the trial and return policies of OTC hearing aids is essential. Many manufacturers offer trial periods for testing devices. For example, some brands provide a 45-day trial period to help users adjust and evaluate effectiveness. Check return conditions, including the timeframe and need for a return number, before purchasing.
Conclusion
Through this exploration, it’s clear that OTC hearing aids offer accessibility and affordability but are not a universal solution. Understanding hearing loss, weighing the pros and cons of OTC devices, and taking essential steps before purchase provide a clear path for users. Professional assessments are crucial for identifying the best hearing assistance and avoiding risks from self-diagnosing or poorly fitted devices. These insights emphasize cautious use of OTC aids and the importance of informed decisions for auditory health.
The discussion around OTC hearing aids goes beyond the devices, focusing on broader implications for individuals facing hearing challenges. It emphasizes the importance of professional guidance, technological empowerment, and careful consideration before purchase. Moving forward, this call to action extends to creating accessibility, awareness, and support for everyone navigating hearing health.
FAQs
1. What are the drawbacks of over-the-counter (OTC) hearing aids?
OTC hearing aids, while more affordable than prescription hearing aids, may still be prohibitively expensive for some. Additionally, they require users to familiarize themselves with new technology to adjust settings. A common issue is that they can amplify background noise, which many users find distracting.
2. What reasons do people have for not using hearing aids?
Many people avoid hearing aids due to stigma and self-perception concerns. They fear appearing old, find devices bulky or uncomfortable, worry about being treated differently, or view needing aids as a weakness.
3. What should you know about over-the-counter hearing aids?
OTC hearing aids are designed for adults who have mild to moderate hearing loss. They are not suitable for children or adults with severe hearing loss or significant auditory challenges. In cases of severe hearing loss, OTC hearing aids may not provide sufficient sound amplification to be effective.
4. How do OTC hearing aids differ from traditional hearing aids?
OTC hearing aids suit those with mild to moderate hearing loss and don’t require a prescription. Traditional hearing aids, prescribed and fitted by an audiologist, are essential for severe hearing loss. They offer tailored solutions for more precise and effective hearing assistance.