These guidelines enable adults over 18 with mild to moderate hearing loss to access affordable hearing aids without a prescription, making hearing care more accessible and empowering consumers to take charge of their auditory health. The availability of OTC hearing aids from big names in retail and online platforms ushers in a new era of hearing support, bridging the gap between the need for assistance and the ability to obtain it easily, thus highlighting the FDA's commitment to consumer empowerment and accessibility in hearing care.
As OTC hearing aids become widely available, consumers are presented with various options, ranging from inexpensive hearing aids to those slightly higher in cost but without the advanced sound technology of prescription aids. This development democratizes the availability of hearing aid technology, ensuring that more individuals can find a solution that fits their lifestyle and budget. It marks a pivotal moment in the transition from traditional hearing aids to a more consumer-friendly approach, where understanding how to navigate the new landscape of FDA-approved, affordable hearing aids will be crucial for millions of Americans seeking to improve their quality of life through enhanced hearing support.
Understanding OTC Hearing Aids
Types and Features of OTC Hearing Aids
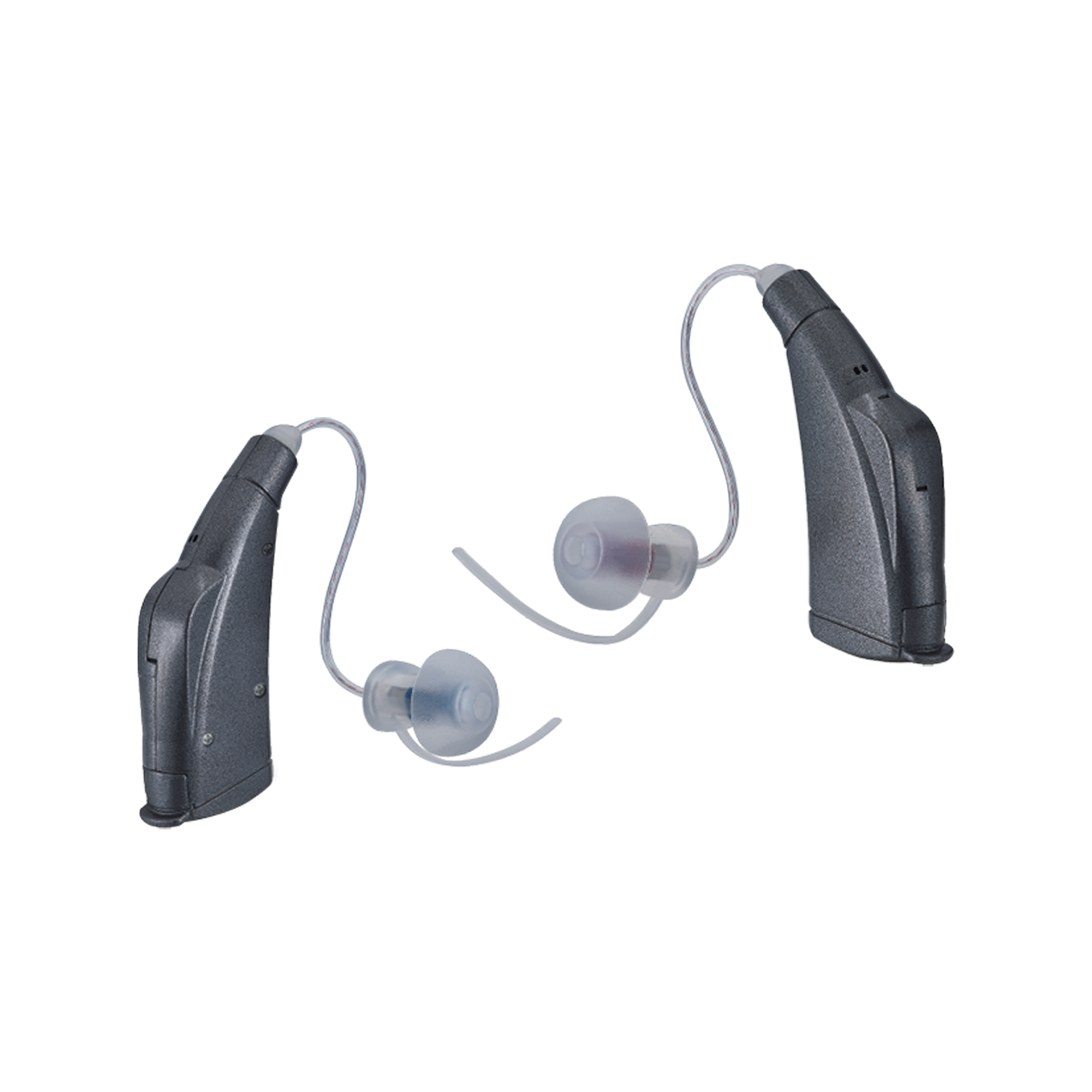
- Basic Types of OTC Hearing Aids: Legacy (traditional) and wireless hearing aids come with essential features like volume control and preset programs.Self-fitting hearing aids offer greater customization through advanced technology, including hearing tests, software, and smartphone apps.
- Device Options: OTC hearing aids are available in two styles: in-the-ear and behind-the-ear, with the latter often better at filtering out background noise.They also come in two types of electronics: analog and digital, catering to different user preferences and needs.
Regulatory Standards and Consumer Guidance
- FDA Oversight: The U.S. Food and Drug Administration regulates OTC hearing aids to ensure they meet safety and effectiveness standards. This includes specific labeling requirements such as warnings, manufacturer's contact information, and details about the device's features and use.
- Purchasing Channels: Consumers can buy OTC hearing aids in-person at stores like Walgreens and Best Buy or through online retailers without a medical exam, prescription, or fitting by an audiologist.
Price Range and Accessibility
- Cost Comparison: OTC hearing aids are significantly less expensive than traditional hearing aids, usually ranging from $200 to $1,000 per pair, compared to $1,000 to over $6,000 for prescription aids.
- Availability: These devices are designed for adults 18 years and older with mild to moderate hearing loss and are not suitable for severe hearing loss or for children.
Consumer Tips
- Usage and Adjustment: It is crucial for users to wear their OTC hearing aids regularly to become accustomed to their features and capabilities.
- Professional Consultation: If users do not experience the expected benefits, they should consider consulting with a hearing health care professional.
- Reporting Issues: Any problems, injuries, or malfunctions should be reported to the FDA through their MedWatch program.
This section provides a comprehensive overview of OTC hearing aids, including their types, regulatory standards, pricing, and tips for consumers to make the most out of these devices.
Understanding Hearing Loss and OTC Hearing Aid Categories
Intended Users and Effectiveness of OTC Hearing Aids
- Eligibility Criteria: OTC hearing aids are designed for adults aged 18 and older who experience mild to moderate hearing loss. This demographic typically struggles with hearing conversations in noisy environments, group settings, or over the phone.
- Functionality: Both OTC and traditional prescription hearing aids utilize similar technologies to capture, amplify, and deliver sounds to the ear, thus aiding those with hearing loss effectively.
Types of Hearing Aids
- Behind-the-Ear (BTE): These are the largest type of hearing aids, suitable for significant hearing loss. They are robust, easy to clean, and may interfere with glasses or masks.
- In-the-Ear (ITE): ITE hearing aids are more discreet, allowing easy access to volume control and battery. They are not recommended for individuals with excessive earwax or those who hear their own voice echoing.
- In-the-Canal (ITC): These devices are almost invisible and easier to keep dry, but are also unsuitable for users with excessive earwax.
Distinguishing Between Sound Amplification Devices and Hearing Aids
- Personal Sound Amplification Products (PSAPs): These devices are intended for situational hearing enhancement and are not regulated. They should not be used as a substitute for hearing aids by those with hearing loss.
- Hearing Aids: Regulated by the FDA, hearing aids are crucial for individuals with age-related or self-perceived hearing loss, designed specifically to improve hearing by amplifying sounds.
Factors to Consider When Choosing OTC Hearing Aids
Key Considerations for Selecting OTC Hearing Aids
- Assessing Medical and Hearing Needs: Individuals with severe hearing loss or complex medical needs should consult an audiologist for a tailored care plan. Those with cognitive or dexterity challenges might find OTC hearing aids unsuitable and should seek professional advice.Before purchasing, check for any medical conditions that require professional attention, such as ear deformities or sudden hearing loss.
- Device Features and Usability: Choose hearing aids that fit well and are comfortable; consider features such as battery life, Bluetooth connectivity, and earwax filters.Evaluate the ease of use, especially if the device requires smartphone integration or specific apps.Look for devices with features that enhance listening in noisy environments such as Digital Noise Reduction and Directional Microphones.
- Cost and Support Considerations: Investigate the cost, warranty, and repair options available for the hearing aids. Opt for devices with a favorable return policy and trial period. Ensure the hearing aid is easy to maintain, preferably with rechargeable batteries and simple operational instructions.
- Professional Consultation and Testing: Consider having a hearing test conducted by a professional to determine the most suitable device for your needs. Check if the device is FDA-approved to guarantee safety and effectiveness.
- Additional Features and Support: Variable Programming and App Control can provide flexibility and convenience by allowing adjustments to be made through a smartphone.Understand the specific environments the device is designed for, such as handling road noise or streaming audio, to manage expectations.
By carefully considering these factors, individuals can choose an OTC hearing aid that best fits their lifestyle and hearing needs, ensuring they receive the maximum benefit from their device.
How to Determine if You're a Candidate for OTC Hearing Aids
Assessing Your Eligibility for OTC Hearing Aids
- Initial Self-Assessment: Evaluate your hearing in daily situations; if you struggle to understand conversations in quiet environments or require high volumes on electronic devices, OTC hearing aids might be beneficial.Consider your comfort with DIY devices; some OTC hearing aids allow user adjustments which require a certain level of comfort and capability.
- Medical Considerations: Exclude medical conditions that necessitate professional care, such as ear discharge, pain, or asymmetric hearing loss, by consulting a physician.Children and those with severe or sudden hearing loss should seek tailored solutions from hearing care professionals.
Professional Evaluation
- Consultation with an Audiologist: A comprehensive hearing test by an audiologist can determine the precise type and degree of hearing loss, guiding the choice between OTC and prescription hearing aids.Regular follow-ups ensure the device continues to meet your hearing needs effectively.
- Risk Assessment: Understand the risks of inadequate sound amplification and the potential for worsening hearing conditions without proper audiologist consultation.Be aware of the limitations of OTC hearing aids for complex hearing issues or higher degrees of hearing loss.
Insurance and Financial Considerations
- Verify if your insurance covers the cost of hearing tests and if it provides any coverage for hearing aids. This can influence the decision between OTC and prescription options.
Identifying Your Hearing Needs
Common Indicators of Hearing Loss
- Difficulty in Distinguishing Words: Recognizing specific words, especially in conversations where background noise is present, can be a significant challenge for those experiencing hearing loss.
- Trouble Following Conversations: If following dialogues in noisy environments or group settings is strenuous, it might indicate a need for hearing support.
- Family History and Occupation: A known family history of hearing loss or employment in high-noise environments are critical risk factors to consider.

Steps to Determine Hearing Aid Needs
- Consultation with a Pharmacist or Specialist: Discussing symptoms with a pharmacist or healthcare provider can help in identifying the need for a detailed hearing assessment.
- Professional Hearing Test: Before purchasing OTC hearing aids, obtaining a hearing test from an audiologist is advisable. This step ensures that the selected device matches the specific hearing loss level and provides guidance on its usage.
Choosing the Right OTC Hearing Aid
Bluetooth Functionality and Expert Guidance
- Bluetooth Capabilities: Modern OTC hearing aids often include Bluetooth technology, allowing users to connect wirelessly to compatible devices such as smartphones and televisions.This feature enhances the user experience by enabling personal sound adjustments and access to multimedia audio directly through the hearing aids.
- Professional Assistance: Consulting with audiologists is crucial as they provide) on selecting the appropriate OTC hearing aid based on individual hearing loss and lifestyle needs.Audiologists can assess whether an OTC hearing aid is suitable and help in customizing settings for optimal performance.
Considerations for Purchase and Support
- Customer Support and Customization: Select companies that offer robust customer support and assistance with customization and troubleshooting of the hearing aids.This support is vital for adapting the device to personal hearing needs and ensuring comfort and effectiveness.
- Return Policy and Warranty: Opt for OTC hearing aids that come with a favorable return policy and a reasonable warranty period.These policies provide a safety net, allowing users to try out the devices and ensure they meet their expectations without financial risk.
Collaborative Care Options
- Pharmacist Consultations: Engage with pharmacists who can evaluate specific hearing challenges and guide the selection of an appropriate OTC hearing device.Pharmacists play a key role in outlining product recommendations based on user preferences and needs, ensuring a tailored hearing solution.
By integrating advanced technology like Bluetooth for enhanced connectivity and relying on professional guidance from audiologists and pharmacists, individuals can make informed decisions when choosing the right OTC hearing aid. This approach not only addresses the functional aspects of hearing aids but also ensures that the devices are tailored to the specific needs and lifestyles of the users.
Getting the Most Out of Your OTC Hearing Aids
Initial Setup and Adjustments
- Self-Management: Setting up and adjusting OTC hearing aids is primarily the user's responsibility, which includes understanding how to operate and adjust the device according to specific hearing needs.
- Learning and Practice: Invest time in learning how the devices function, including how to insert them, change batteries, and clean them. Regular use in various environments helps familiarize their features and controls.
Enhancing Device Performance
- Utilizing Technology: Future models of OTC hearing aids are expected to integrate advanced technologies like AI, AR, and biometric sensors, enhancing user interaction and performance.
- Minimizing Interference: To reduce wind noise, covering the microphones can help maintain sound quality. Additionally, turning off background noises, such as a radio or TV, can improve clarity during phone calls.
Regular Maintenance and Professional Support
- Audiologist Involvement: Even though OTC, regular check-ins with an audiologist are crucial to ensure the hearing aid is effectively meeting your hearing needs and to check for any changes in hearing ability.
- Professional Help: If issues persist or adjustments are needed, seeking professional support or consulting the manufacturer's troubleshooting resources is recommended.
Usage Tips for Optimal Experience
- Adaptation Period: Allow time to get accustomed to the new hearing aid, as it takes practice to fully benefit from its capabilities. Wearing them regularly helps in adjusting to how they amplify sound.
- Sound Management: Learn to manage the level of noise and make connections between what you hear and see, which can significantly enhance the hearing experience.
Support and Follow-Up
- Customer Support: Choosing companies that offer strong customer support, including phone-based or online help, can be beneficial for troubleshooting and general queries.
- Continued Care: Scheduling follow-up appointments or consultations can ensure the device continues to meet your needs and adjustments are made as required.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting Common Issues
Regular Maintenance Procedures
- Daily Cleaning: Remove wax or debris buildup and wipe down the entire device daily to ensure optimal performance.
- Weekly Cleaning: Follow thorough cleaning protocols for In-the-Ear (ITE) and Behind-the-Ear (BTE) hearing aids, including using a brush, slim tube cleaning tool, earmold tubing blower, and microfiber cloth.
- Professional Cleanings: Schedule professional cleanings approximately every six months; these typically cost between $30 and $60.
OTC Hearing AidsTroubleshooting Common Issues
- Power and Sound Quality: If experiencing weak or no sound, check for clogged devices or low battery and replace batteries as necessary.For whistling or feedback issues, ensure the hearing aid is properly inserted. If the problem persists, check for wax or debris blockage or improper fitting.
- Physical Fit and Comfort: If the hearing aid slips out, adjust the size of the dome or consider adding a retention wire to accommodate moisture in the ear canal or movement.For discomfort or pain, ensure proper insertion and check for wax buildup. If issues continue, the hearing aid shell might require modifications.
Safe Handling and Care Practices
- Avoid Misuse: Never place hearing aids in microwaves or ovens, and avoid attempting to open the casing or tampering with the wiring.
- Cleaning Tools: Only use tools specifically designed for hearing aid maintenance, and avoid using inappropriate cleaning methods.
Professional Support and Education
- Audiologist Consultations: Purchasing from an audiologist often includes ongoing support such as adjustments, repairs, and professional cleaning.Regular follow-ups with a hearing care provider ensure that the hearing aids function optimally and any necessary repairs are handled promptly.
- Education on Care: Before purchasing an OTC hearing aid, ensure you receive proper education on device care from an audiologist.
Ear Care for Hearing Aid Users
- Keeping Ears Clean: Maintain ear hygiene to prevent contaminants from affecting the hearing aids. Safe earwax removal methods include using a cotton ball with water, saline, or hydrogen peroxide, or a bulb syringe for rinsing.
How to Purchase and Fit OTC Hearing Aids
Purchasing OTC Hearing Aids
- Selecting a Purchasing Venue: OTC hearing aids can be acquired from a variety of locations including local pharmacies, grocery stores, and some chain stores. Online options are plentiful with retailers like Amazon, Best Buy, CVS, Sam's Club, Target, Walgreens, and Walmart offering these devices.
- Price Considerations: It's important to budget accordingly as OTC hearing aids typically range from $200 to $1,000 per pair, making them a more affordable option compared to prescription aids which can cost between $1,000 and over $6,000.
- Professional Evaluation Recommended: Before making a purchase, it is advisable to visit a healthcare provider or an audiologist for a hearing evaluation to ensure the selected device is suitable.
Fitting and Adjusting Your OTC Hearing Aids
- Initial Setup: Upon purchasing, some OTC hearing aids may require self-fitting. Audiologists can assist in customizing and testing these devices to ensure optimal performance.
- Adjusting to Your Needs: It's crucial to adjust communication styles to enhance the hearing aid experience. This includes ensuring your face is visible when speaking, reducing background noise, and using support tools like written instructions.
- Utilizing Professional Services: After purchasing, ongoing support such as customization, cleaning, and counseling from audiologists can significantly enhance the effectiveness of OTC hearing aids.
Ensuring Effective Use
- Trial Periods and Warranties: Always inquire about trial periods to test the hearing aids in everyday environments, ensuring they meet your needs. Additionally, check for warranties that can provide peace of mind and protect your investment.
- Plan for Future Needs: Consider how your hearing might change in the future and whether the hearing aid can accommodate these changes.
- Avoiding Misleading Claims: Be vigilant about misleading claims and ensure that the hearing aids purchased have clear, factual information about their capabilities.
By following these guidelines, individuals can make informed decisions when purchasing and fitting OTC hearing aids, leading to better hearing experiences and overall satisfaction.
Conclusion
The transition to OTC hearing aids signifies a monumental shift towards making hearing care more accessible and affordable for adults with mild to moderate hearing loss. By encapsulating the crucial aspects of selecting, purchasing, and maintaining OTC hearing aids, this guide has aimed to empower individuals to navigate this new landscape effectively. The emphasis on consultation with audiologists, even when opting for OTC models, underscores the importance of professional guidance in ensuring that individual hearing needs are met optimally, thereby enhancing life quality through improved hearing.
As the domain of hearing aids continues to evolve, with advancements such as Bluetooth connectivity and potentially AI-driven technologies, users are encouraged to remain informed and proactive in managing their hearing health. Recognizing the significance of these developments not only facilitates a smoother transition for new users but also highlights the broader implications for societal views on hearing care. It positions consumer empowerment and accessibility at the forefront, promising a future where hearing support is seamlessly integrated into daily life, ensuring that individuals do not have to navigate the journey to better hearing alone.
OTC Hearing Aids FAQ
- What advancements in hearing aid technology can we expect in 2026? In 2026, it is anticipated that hearing aids will incorporate advanced AI algorithms that improve their ability to automatically adjust settings, especially in noisy environments. Additionally, some models are expected to include features that monitor vital signs and may even help in early detection of health issues, such as high blood pressure.
-
How much should I expect to pay for an over-the-counter hearing aid? The cost of OTC hearing aids can vary widely, ranging from as low as $59 per pair to upwards of $3,000 per pair. The price depends on the features and technology included in the hearing aids.