For many people beginning their hearing-health journey, one of the first questions is:
“Should I use bone conduction devices or traditional air-conduction hearing aids?”
Both options help you hear more clearly, but they work in very different ways. Understanding those differences — along with your lifestyle, comfort preferences, and type of hearing difficulty — can make the decision much easier.
This guide breaks down:
- How each technology works
- Who each device is best suited for
- Comfort, sound quality, and daily-use considerations
- Pros, cons, and lifestyle fit
- When to choose bone conduction vs. traditional hearing aids
If you’re comparing products like Mimitakara bone conduction open-ear hearing devices with standard hearing aids, this article gives you a clear, simple roadmap.
1. How Hearing Devices Work: Bone Conduction vs. Air Conduction
Before choosing a device, it’s helpful to understand the fundamental difference between these two technologies.
Traditional Hearing Aids: Air Conduction
This is the most common type of hearing support used today. They amplify sound in the air and deliver it through the ear canal.
How they work:
- Microphones pick up sound . Amplifiers boost speech frequencies . Sound travels through the ear canal . The eardrum and inner-ear structures process it . The auditory nerve sends signals to the brain
These hearing aids rely on the natural hearing pathway.
Best for:
- Age-related hearing difficulty
- Noise-induced hearing loss
- Mild to moderate hearing loss
- Users who need clearer speech in daily conversation
Examples: Behind-the-ear (BTE), receiver-in-canal (RIC), in-ear devices.
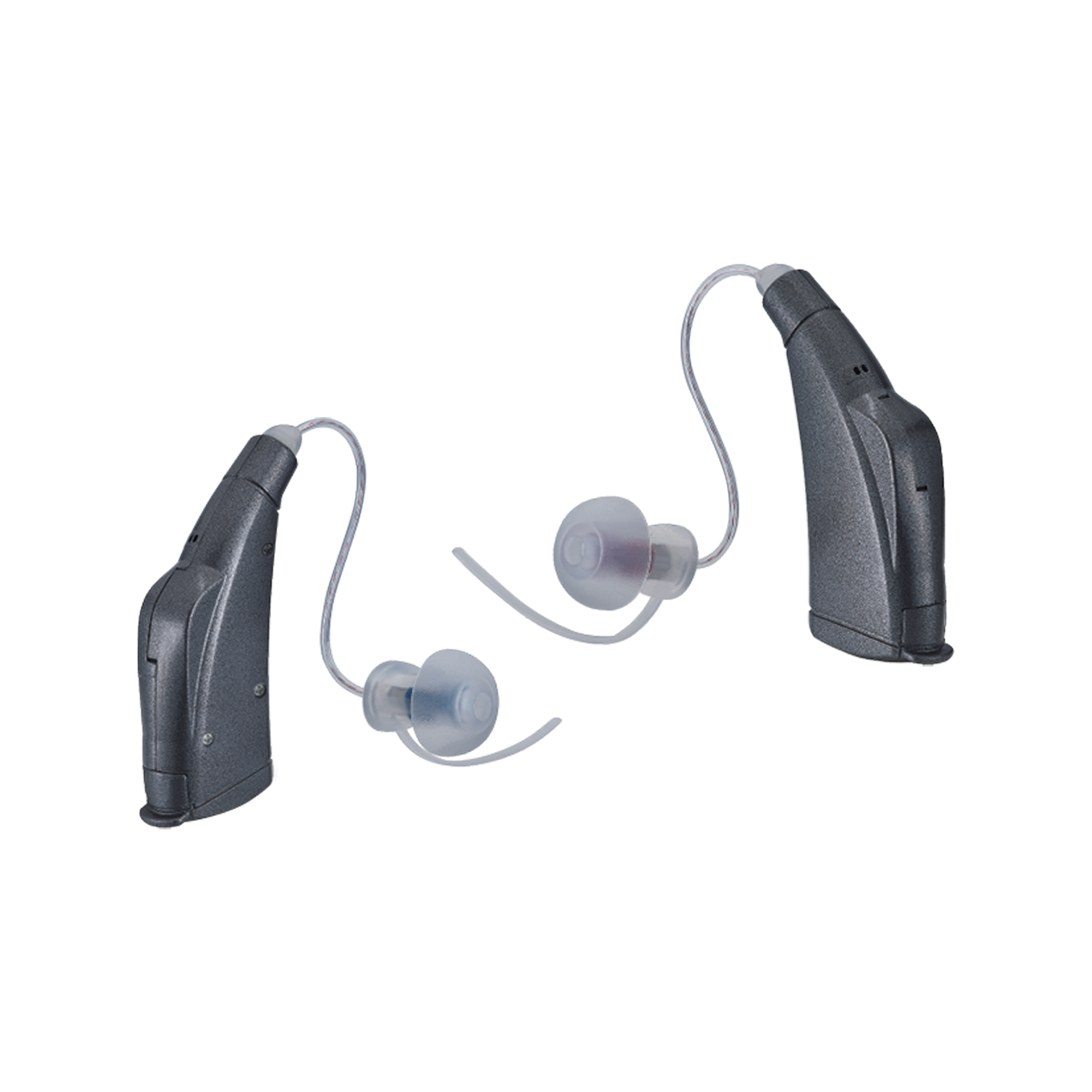
Bone Conduction Hearing Devices: Bypass the Ear Canal
Bone conduction technology sends sound through vibrations, traveling directly to the inner ear via the bones of the skull.
How they work:
- Device sits on the cheekbone or temples
- Transducers create gentle vibrations
- Vibrations bypass the eardrum entirely
- Sound reaches the cochlea through bone pathways
- The brain interprets those signals as sound
There is no obstruction in the ear canal — leaving your ears open to the environment.
Best for:
- People with conductive hearing issues
- Ear canal irritation or sensitivity
- Blocked ears due to wax, allergies, or chronic infections
- Individuals who prefer open-ear comfort
- Active lifestyles (cycling, jogging, office multitasking)
2. Key Differences at a Glance
| Category | Bone Conduction Devices | Traditional Hearing Aids |
| Pathway | Sound through bone vibrations | Sound through the ear canal |
| Ear Canal | Fully open | Partially or fully occluded depending on style |
| Best For | Conductive issues, sensitive ears, active users | Age-related or sensorineural hearing loss |
| Comfort | No occlusion, no pressure | Small in-ear or behind-ear components |
| Sound Quality | Natural environmental awareness | High clarity and directional amplification |
| Background Noise | Hearing remains open to the environment | More noise-filtering control |
| Style | Frames, headbands, or open-ear hooks | RIC, BTE, or in-ear designs |
| Streaming | Yes (depending on model) | Yes, varies by model |
Both are effective — the main difference is how you want to hear and what your ears are most comfortable with.
3. Who Bone Conduction Devices Are Best For
Bone conduction devices shine in certain scenarios. They’re especially useful for people who:
3.1 Have Ear Conditions or Sensitivities
Great for people who experience:
- Ear canal irritation
- Eczema or dermatitis in the ear
- Chronic infections
- Excessive earwax
- Pain with in-ear devices
Because bone conduction bypasses the ear canal entirely, there’s no occlusion or pressure.
3.2 Want Open-Ear Comfort and Natural Awareness
Bone conduction keeps your ears fully open, making it easier to:
- Hear traffic while jogging
- Hear your surroundings during office work
- Maintain conversation during outdoor activities
- Avoid the “plugged ear” feeling
It’s essentially a hearing enhancement system that doesn’t block the ear.
3.3 Prefer Lightweight, Active-Friendly Devices
Many users choose bone conduction for:
- Cycling
- Walking
- Running
- Gym workouts
- Outdoor sports
- Hands-free work environments
Open-ear listening + stable frames = reliable all-day comfort.
3.4 Have Conductive Hearing Loss
Individuals with issues affecting the eardrum or middle ear often experience improved clarity with bone conduction, since it bypasses the damaged pathway.
3.5 Need Clearer Speech Without Ear Canal Pressure
Some people simply dislike the sensation of in-ear devices. Bone conduction offers:
- No insertion
- No rubbing
- No tight seal
- No in-ear fatigue
The comfort difference is meaningful for long-term wear.
4. Who Traditional Hearing Aids Are Best For
Traditional air-conduction devices remain the standard for most hearing needs.
4.1 Best for Sensorineural or Age-Related Hearing Loss
If your inner ear’s hair cells need support, a traditional hearing aid may be more appropriate because it:
- Amplifies speech frequencies
- Filters noise
- Refines clarity
- Uses advanced digital processing
These technologies are ideal for speech-focused environments like restaurants, meetings, and family gatherings.
4.2 Great for People Who Need Directional Sound Control
Air-conduction hearing aids offer features such as:
- Noise reduction
- Directional microphones
- Speech enhancement algorithms
- Adaptive feedback suppression
These are powerful tools for conversational listening in noisy places.
4.3 Perfect for Subtle, Nearly Invisible Wear
Many people prefer the discreetness of:
- Receiver-in-canal devices
- Micro in-ear designs
- Skin-tone BTE styles
If cosmetic appearance matters, traditional hearing aids offer more “hidden” options.
5. Sound Quality Comparison: Which Sounds More Natural?
Both options offer clear sound — but each has a distinct listening experience.
Bone Conduction Sound: Open, Ambient, Natural
Pros:
- You hear your environment as it truly is
- No muffling of your natural hearing
- Clear understanding of speech in quiet or moderate environments
Cons:
- More outside noise enters your listening space
- Vibrational sound feels different from traditional audio
- Not ideal for severe hearing loss
Great for everyday speech and environmental awareness.
Traditional Hearing Aid Sound: Focused, Amplified, Speech-Optimized
Pros:
- Excellent clarity for conversations
- Reduced background noise
- Enhanced directionality
Cons:
- Some users feel “plugged up” at first
- Takes a few days to adapt
- Sound may feel “closer” or louder depending on settings
Ideal for people who want focused and controlled hearing support.
6. Comfort & Lifestyle Comparison
Comfort can be just as important as sound.
Bone Conduction Comfort Advantages
- Nothing inside the ear
- Zero pressure or occlusion
- Breathable and sweat-friendly
- Good for long hours of wear
- Lightweight and headband-based styling
- Glasses + masks + hearing devices = no conflict
Traditional Hearing Aid Comfort Advantages
- Multiple sizes to fit your ear shape
- Soft, medical-grade materials
- Secure behind-the-ear placement
- Comfortable for all-day indoor use
- Better for people sitting at desks or working in quiet environments
7. Which Is Better for Calls, TV, and Daily Communication?
Modern devices enhance your lifestyle in different ways.
Bone Conduction
- Excellent for multitasking
- Great for people who prefer open ears during calls
- Natural sound for one-on-one conversations
- Comfortable for TV watching without blocking ambient sounds
Traditional Hearing Aids
- Better for speech clarity
- Enhanced digital noise reduction
- More refined sound processing
- Ideal for noisy environments, restaurants, or group settings
8. Pros & Cons Summary
Bone Conduction Devices (e.g., Mimitakara Open-Ear Models)
Pros
- Open-ear comfort
- Great for active lifestyles
- Lightweight and sweat-friendly
- No ear canal pressure
- Works for some conductive hearing issues
- Safe, natural environmental awareness
Cons
- Not suitable for severe hearing loss
- More ambient noise
- Vibrational feel takes getting used to
Traditional Hearing Aids
Pros
- Best for age-related and sensorineural hearing loss
- Rich sound customization
- High speech clarity
- Directional sound features
- Discreet design options
Cons
- Ear canal may feel plugged
- Sweat and moisture can affect performance
- May require more maintenance
9. So… Which One Should You Choose?
Here’s a quick guide:
Choose Bone Conduction If:
- You want open-ear comfort
- You exercise or stay active
- Your ear canal gets irritated easily
- You want a lightweight, breathable device
- You prefer natural environmental awareness
- You have conductive hearing issues
Choose Traditional Hearing Aids If:
- You have sensorineural or age-related hearing loss
- You want clearer speech in noisy environments
- You want more digital sound processing
- You prefer discreet behind-the-ear or in-ear designs
- You struggle with conversation clarity at work or in groups
10. Mimitakara Options: Choosing Your Ideal Device
Mimitakara offers support for different lifestyles and hearing preferences.
Mimitakara Bone Conduction — Great for Open-Ear Comfort
- Lightweight and comfortable
- Open-ear listening
- Stable design for active lifestyles
- Ideal for mild hearing needs or conductive issues
Perfect for users who want hearing enhancement without putting anything in their ear canal.
Mimitakara Traditional Hearing Aids — Great for Speech Clarity
- Behind-the-ear designs
- Tailored for speech in conversations
- Natural, balanced amplification
- Comfortable for everyday use
Best for users who prioritize conversation clarity, especially in group settings.
Conclusion: The Right Hearing Device Depends on Your Comfort, Needs, and Lifestyle
There is no “one best choice” — only the best choice for you.
Bone conduction devices offer breathable, open-ear comfort and natural awareness. Traditional hearing aids provide refined amplification and strong speech clarity. The right option depends on how you live, what environments you’re in, and what feels good on your ears.
No matter which path you choose, Mimitakara offers user-friendly devices designed to support your everyday hearing — whether you’re working, exercising, relaxing, or connecting with family.